Artery occlusion
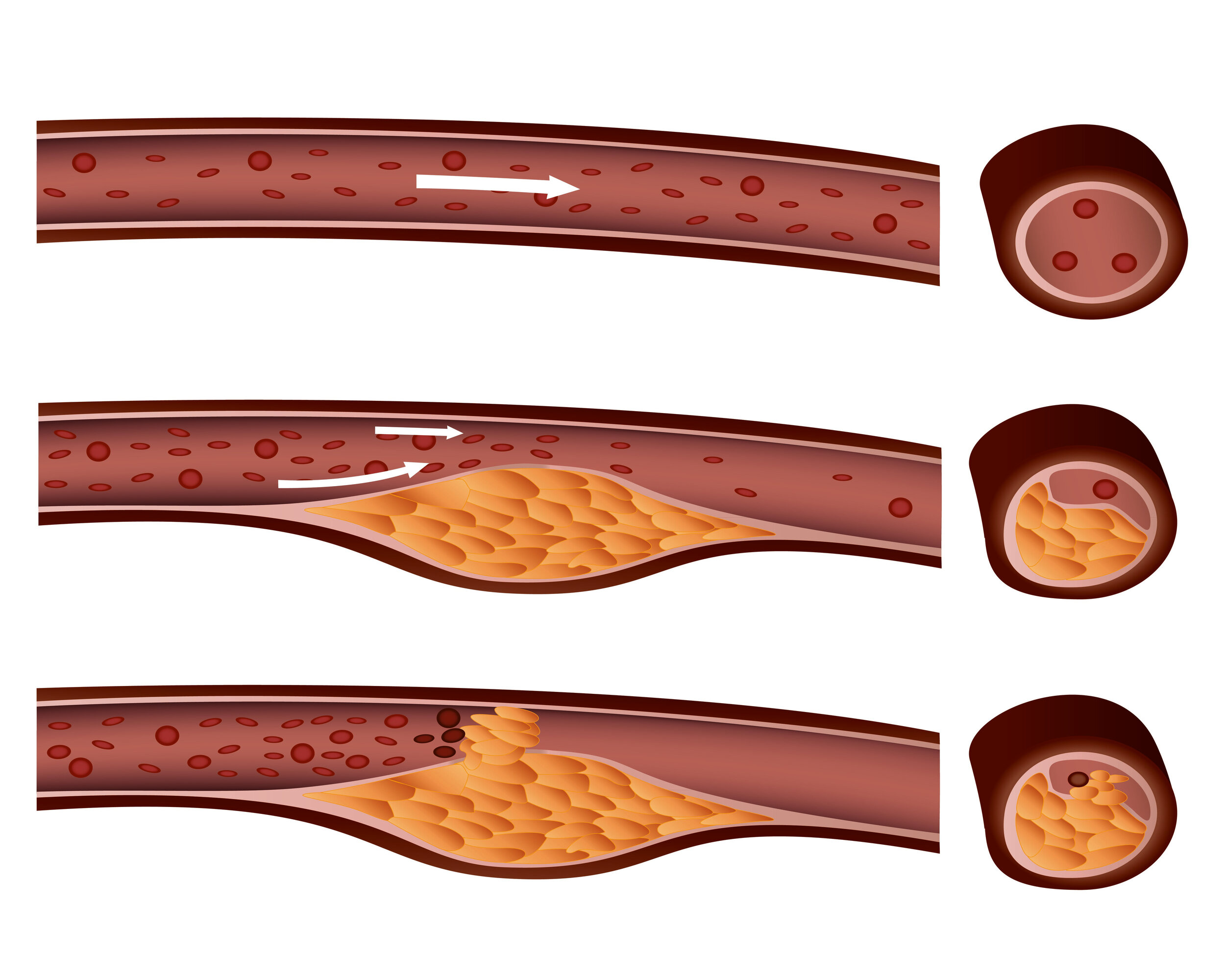
An arterial occlusion is the final stage of a pronounced arteriosclerosis. In the case of the so-called smoker’s leg, this is an arterial occlusion in the leg. In the case of arterial occlusion in the leg, a distinction must always be made between chronic arterial occlusion and acute arterial occlusion. Depending on the course and cause of the arterial occlusion, there are different clinical manifestations:

Arterial occlusion symptoms in acute occlusion may include nocturnal pain when lying down in the area of the feet, acute cold sensation with paling of the extremity or sudden pain when walking, immobilizing after a few meters. In the case of acute arterial occlusion in the legs, there is usually a sudden onset of discomfort or already existing pain suddenly worsens. In the case of chronic arterial occlusion, the symptoms have often existed for a long time and the patient can usually cope with them in everyday life.
The difference between an acute and a chronic arterial occlusion is usually collateralization: in a chronic occlusion, the body has often had enough time to form bypasses, collaterals. If a vessel is acutely occluded, there is no other route for the blood to travel, and the leg is suddenly deprived of adequate oxygen. If the oxygen debt is so great that the leg is in danger of being damaged, immediate action must be taken: the occluded vessel must be reopened. This can usually be done with a catheter intervention. Depending on the localization, however, an arterial occlusion may also have to be treated by surgery.
Chronic occlusion can often remain clinically asymptomatic with good collateral formation. In this case, arteriosclerosis treatment is essential to maintain the status. Therefore, structured walking training also plays a major role in PAOD therapy: regular walks (3 x 30 min. per week) stimulate angiogenesis, i.e. new vessels sprout and surround the occluded vessel segment – similar to a bypass – so that blood flow to the periphery is maintained. The walking distance can thus be significantly improved. This is how circulatory disorders can be treated in the leg area. In stroke treatment, the therapy is primarily with medications in order to reduce the vascular risk factors and blood thinning medications, although collateral circulation can also form here.
What is meant by an arterial occlusion?
In the case of an arterial occlusion, a vessel segment is completely blocked and the blood flow is thus interrupted. Vascular occlusions can affect the entire vascular system. Either a local occlusion occurs on the basis of arteriosclerosis with mostly carry-over of material to the periphery, or the vessel occlusion is caused by an embolism: In chronic atrial fibrillation, small thrombi are formed in the heart and are washed further with the blood flow and become entangled in the vascular system. Depending on the localization, this can result in a stroke or acute limb ischemia.